The molluscum virus is actually a form of pox virus, which sounds scary because we think of things like small pox and chicken pox when we hear that. Like those viruses, the molluscum contagiosum virus is highly contagious but unlike them, it is not a potentially deadly virus. Symptoms of the molluscum virus may be unpleasant but they do not cause serious harm; still, most people want treatment for the condition.
Molluscum Contagiosum Virus Symptoms
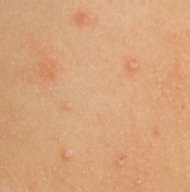
The primary symptom of molluscum contagiosum is small bumps on the skin. The bumps may be flesh-colored or light tan or pink. Sometimes small blood vessels become enlarged, which make the bumps more of a red color. If you look closely, you may see a small, pinhole-sized opening in the center of the bumps. If you squeeze them, the core may come out, just like when you squeeze a whitehead (squeezing them is not advised, though; it can lead to irritation or even infection, as well as causing the condition to spread). There may be just one or two bumps in an area or there may be more than two dozen. The skin around the bumps may become dry and flaky.
The bumps can appear anywhere on the body but are most likely to appear on the arms, legs, face, neck and torso. The condition is seen in children more often than in adults, but adults can develop it, as well. Those with compromised immune systems are especially susceptible.

Often the appearance of this characteristic rash is the only symptom of molluscum contagiosum, but sometimes itching also occurs. Itching may vary in severity from slight to significant.
Molluscum contagiosum is sometimes mistaken for ordinary acne or for warts. Click here to learn more about warts and how to recognize them; you’ll see that while similar, they do differ in some key ways from molluscum contagiosum.
How Does the Molluscum Virus Spread?
The molluscum virus is very contagious. It can be spread by direct person-to-person contact but also by indirect contact, such as when an infected person shares clothing, towels or washcloths with someone else. It is also possible to spread the virus from one area of your body to another when shaving, scratching or otherwise touching an infected area and then touching another area. The ease with which it is spread can make it difficult to treat the condition.
Molluscum Contagiosum Virus Treatment
The molluscum contagiosum virus is often treated by physicians the same way warts are treated. (Click here for wart removal information). The bumps may be frozen off (cryotherapy), burned off (electrocautery), surgically removed or treated with chemotherapy cream. Occasionally molluscum contagiosum is treated with laser therapy. As you might imagine, many people want to avoid these potentially painful, expensive treatments.
Some people decide not to treat their molluscum contagiosum at all but to just wait for the bumps to go away on their own. If you can avoid spreading the condition to other parts of your body, the condition may in fact go away eventually even without treatment, but that can take a long time. Many people are too self-conscious about the appearance of all the bumps to wait that long, and those that experience itching from the condition definitely want prompt treatment.
Recommended Product for Treating Molluscum Contagiosum Virus
We recommend treating the molluscum virus with a natural product like Naturasil Molluscum, which contains antiviral compounds from the extracts of plants. It is very effective, and there is no risk of scarring, a fairly common side effect of cryotherapy and other aggressive treatments. You can follow this link to the Naturasil Website to learn more.
More on the Molluscum Virus on our Main Skin Molluscum Page
Healthy Skin Guide Home Page